Calculation of the temperature field in the ingot is an essential component of the remelt simulators. Both electrode and ingot domains are calculated subject to the specified boundary conditions with results being presented in text, CSV or VTK file formats.
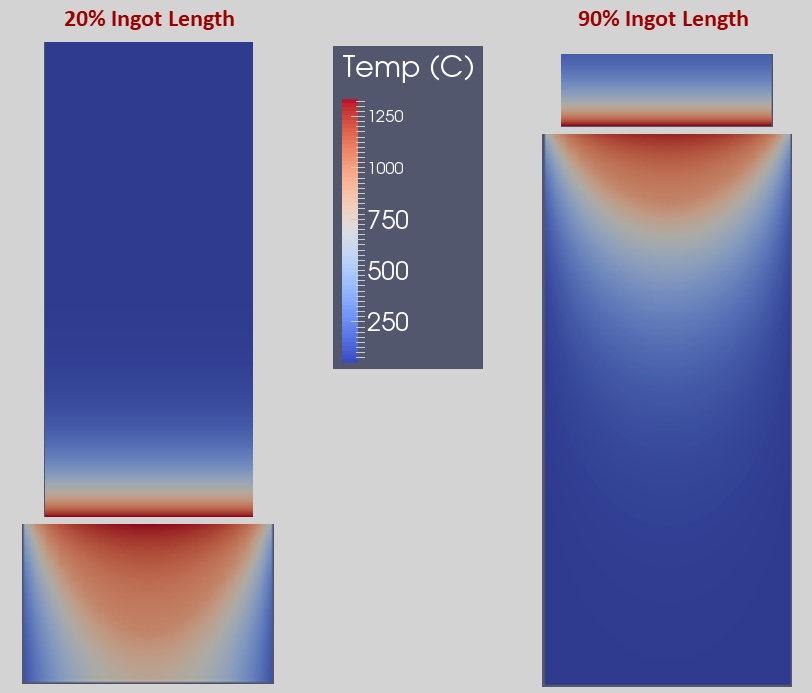
From the time-dependent changes in ingot temperatures, the ingot solidification conditions are evaluated and presented as either a PROFILE or a MAP as discussed on the Solidification page.
ESR slag temperatures are defined by a characteristic slag temperature and a specified temperature distribution within the slag. This characteristic temperature is defined by the slag resistance which is necessary to close the slag heat balance while simultaneously satisfying Ohm’s law across the slag.
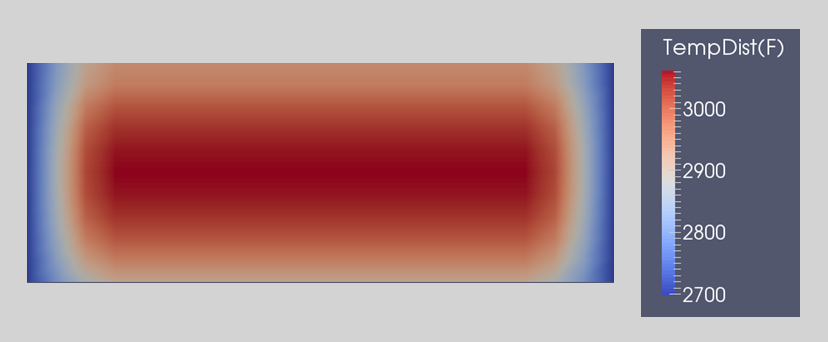
The figures below show slag and ingot temperature distributions at various stages of melting. As the melt rate drops due to reduced power input toward the end of melting, the pool shrinks as both slag and ingot temperatures drop. After power off, both ingot and slag continue to cool with the final solidification point being in the lower central region of the slag for both round and slab ingots.
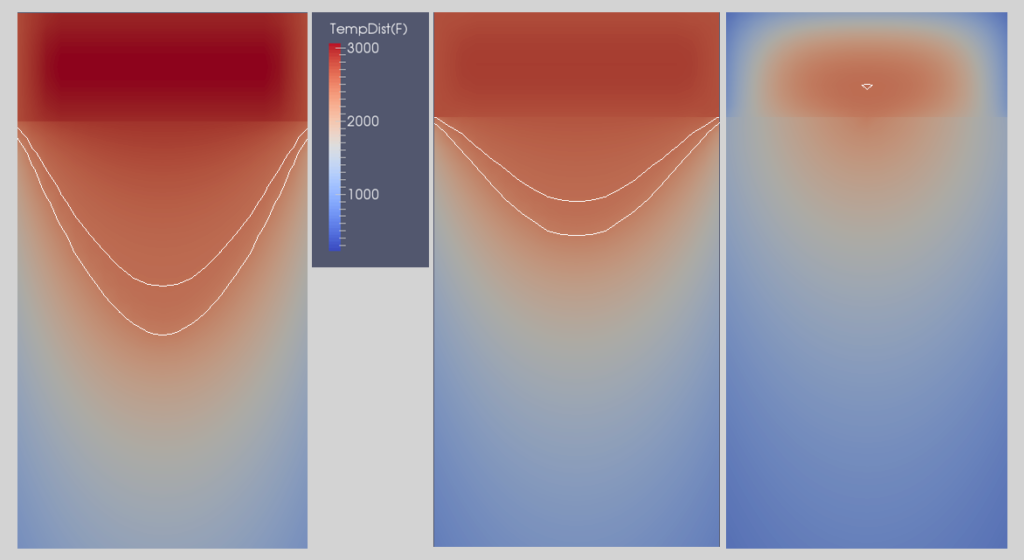
for a Cylindrical ESR Ingot

for a Slab ESR Ingot